고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문 제목
코드카데미 Javascript - 반복 메서드 (forEach, map, filter, findIndex, reduce, some, every)
본문

.forEach( )
-
배열.forEach(콜백함수);
-
같은 코드를 배열의 각 요소에 적용시켜먼서 실행함
-
인자로 콜백함수를 전달받음
-
콜백 함수의 형태는 함수 선언 혹은 화살표 함수
-
미리 콜백 함수를 선언했다면 함수의 이름만 전달해도 됨
-
-
forEach()의 리턴값은 늘 undefined임
const fruits = ['mango', 'papaya', 'pineapple', 'apple'];
fruits.forEach(fruits => console.log(`I want to eat a ${fruits}`));
콜백함수로 화살표 함수를 사용한 모습
.map( )
-
배열.map(콜백함수);
-
각 배열의 요소를 적용하며 같은 코드를 반복함
-
콜백함수를 인자로 받고 새로운 배열을 리턴함 (원래 배열은 변화X)
const animals = ['Hen', 'elephant', 'llama', 'leopard', 'ostrich', 'Whale', 'octopus', 'rabbit', 'lion', 'dog'];
// Create the secretMessage array below
const secretMessage = animals.map(animal => animal[0]);
console.log(secretMessage.join('')); // HelloWorld
const bigNumbers = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500];
// Create the smallNumbers array below
const smallNumbers = bigNumbers.map(number => number/100);
console.log(smallNumbers); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
1. animals라는 배열에 들어있는 문자열의 앞 글자를 따서 secretMessage라는 새로운 배열을 만듬
2. bigNumbers의 값들을 100으로 나눠 smallNumbers라는 새로운 배열을 만듬
.filter()
-
배열.filter(콜백함수)
-
특정 조건에 참이 되는 배열의 요소를 리턴한다
const randomNumbers = [375, 200, 3.14, 7, 13, 852];
// Call .filter() on randomNumbers below
const smallNumbers = randomNumbers.filter(value => value< 250 );
const favoriteWords = ['nostalgia', 'hyperbole', 'fervent', 'esoteric', 'serene'];
// Call .filter() on favoriteWords below
const longFavoriteWords = favoriteWords.filter(word => word.length> 7);
1. randomNumbers에서 250 보다 적은 값들만 리턴해서 smallNumbers라는 새로운 배열 생성
2. 7글자 이상인 문자들만 리턴해서 longFavoriteWords라는 새로운 배열 생성
.findIndex( )
-
배열.findIndex(콜백함수)
-
특정 조건에 참이 되는 첫번째 요소의 인덱스를 리턴함
-
만약에 조건을 만족하는 값이 없다면 -1을 리턴함
const animals = ['hippo', 'tiger', 'lion', 'seal', 'cheetah', 'monkey', 'salamander', 'elephant'];
// Find the index of 'elephant' in the animals array
const foundAnimal = animals.findIndex(animal => animal==='elephant');
console.log(foundAnimal); // 7
// Find the animal that starts with 's'
const startsWithS = animals.findIndex(animal => animal[0]==='s');
console.log(startsWithS); // 3
1. elephant와 일치하는 값을 찾아서 그 인덱스를 리턴
2. s로 이름이 시작하는 동물을 찾아서 그 인덱스를 리턴
.reduce( )
-
배열.reduce(콜백함수, 초기값)
-
배열 전체를 돌면서 주어진 콜백함수를 실행하고 하나의 값을 리턴함 (그럼으로써 배열을 reducing 함)
-
콜백함수를 인자로 받음. 두번째 파라미터인 초기값은 전달해도 안 해도 됨
-
콜백함수는 두 개의 파라미터를 가짐
const numbers = [1, 2, 4, 10];
const summedNums = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue
})
console.log(summedNums) // Output: 17
위 코드가 실행되는 동안 각 값이 변화하는 과정
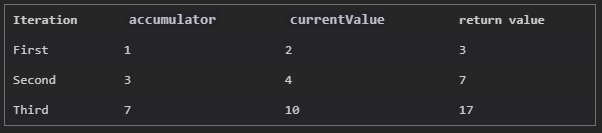
1. accumulator = 배열의 첫번째 값, currentValue = 배열의 두번째 값
2. 두번째 실행부터 이전 return value가 accumulator가 됨. currentValue는 배열의 그 다음 값
const numbers = [1, 2, 4, 10];
const summedNums = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue
}, 100) // <- Second argument for .reduce()
console.log(summedNums); // Output: 117
두번째 파라미터로 100을 전달한 경우
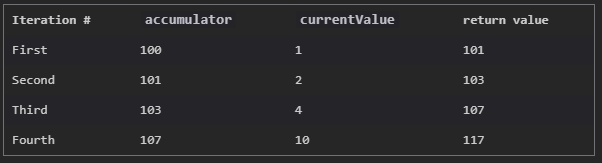
1. accumulator = 100, currentValue = 배열의 첫번째 값
2. 두번째 실행부터 이전 return value가 accumulator가 됨. currentValue는 배열의 그 다음 값
.some( )
-
배열.some(콜백함수)
-
적어도 배열의 요소 중 하나가 조건을 만족하는지 확인함
-
참 혹은 거짓을 리턴한다
-
콜백함수에는 반드시 하나의 파라미터가 있어야 함
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// checks whether an element is even
const even = (element) => element % 2 === 0;
console.log(array.some(even));
// expected output: true
.every( )
-
배열.every(콜백함수)
-
배열의 모든 요소가 내가 정한 조건을 만족하는지 확인함
-
그렇다면 참 아니라면 거짓을 리턴함
const isBelowThreshold = (currentValue) => currentValue < 40;
const array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(array1.every(isBelowThreshold));
// expected output: true
'IT > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코드카데미 Javascript - 클래스와 인스턴스, 상속, 정적 메소드 (0) | 2020.09.27 |
|---|---|
| 코드카데미 Javascript - 객체와 this, 게터 & 세터, 내장객체 메소드 (0) | 2020.09.26 |
| 코드카데미 Javascript - 고차함수와 콜백함수 (0) | 2020.09.24 |
| 코드카데미 Javascript - 배열 메서드 (push, pop, shift, slice, indexOf) (0) | 2020.09.23 |
| 코드카데미 Javascript - Scope (블럭스코프, 사용시 장점) (0) | 2020.09.22 |





댓글 영역